Laparoscopic Surgery


Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally Invasive Innovations in Modern Medicine
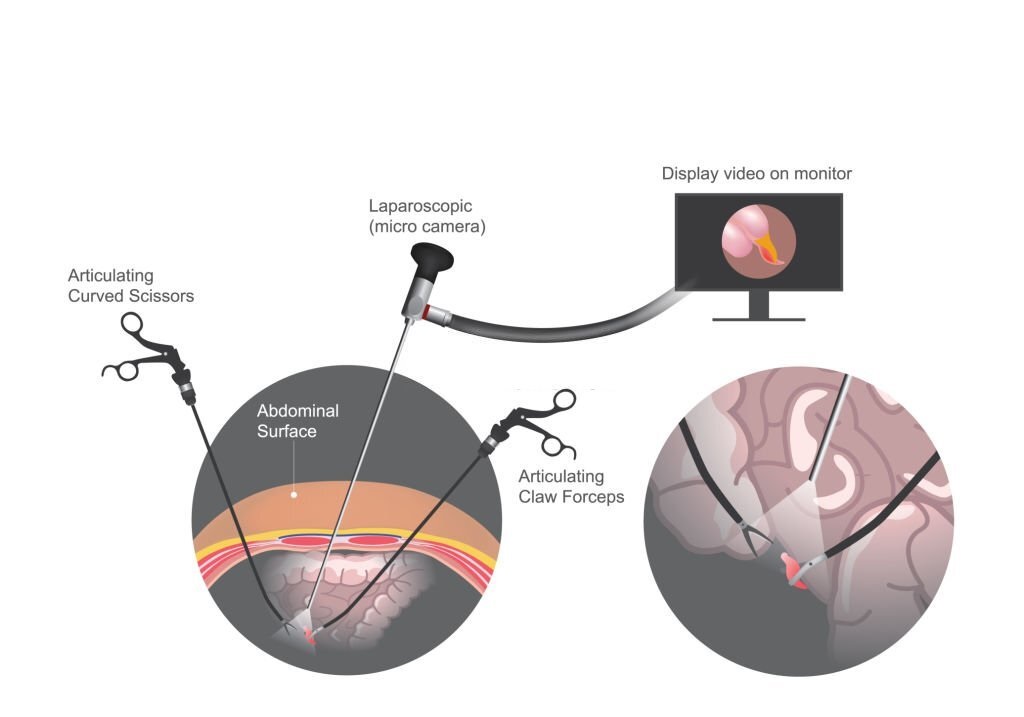
Laparoscopic surgery, also referred to as minimally invasive or keyhole surgery, is an advanced surgical approach enabling the execution of diverse procedures through smaller incisions in contrast to conventional open surgery. This technique employs specialized instruments and a laparoscope—a slender, illuminated tube housing a camera—to observe and carry out operations on internal organs.
Safety Matters: Examining the Security of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery maintains an equivalent level of safety to traditional open surgery. At the outset of a laparoscopic procedure, the laparoscope is introduced through a minor incision adjacent to the belly button (umbilicus). Initially, the surgeon examines the abdomen to evaluate the feasibility of conducting laparoscopic surgery safely. If substantial inflammation is present or if other factors impede a clear view of structures, the surgeon might need to make a larger incision to complete the procedure securely.
Like any form of intestinal surgery, certain risks, including complications associated with anesthesia, bleeding, or infections, are inherent. The risk inherent to any operation is influenced, in part, by the specific nature of the procedure. An individual’s overall health and underlying medical conditions also contribute to the risk associated with any operation. It’s advisable to engage in a discussion with your surgeon to assess your personalized risk profile for the intended operation.