Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery


Surgical Solutions for Hernias: Navigating the Path to Recovery
Laparoscopic hernia surgery, also referred to as minimally invasive hernia repair, is a surgical method employed for hernia correction. Hernias materialize when an organ, often the intestine, protrudes through a weakened section of the abdominal wall. During laparoscopic hernia surgery, minor incisions are crafted in the abdominal region, and a laparoscope (a slender, flexible tube with a camera) guides the surgical instruments.
Types Of Hernia & Treatment
An inguinal hernia arises when fatty tissue or a section of the intestine pushes through the abdominal wall or into the inguinal canal located in the groin area. This is the prevailing form of hernia, more commonly observed in men compared to women.
Femoral hernias emerge when the intestine pushes through the canal that accommodates the femoral artery and vein, extending into the upper thigh. Due to the broader bone structure, femoral hernias primarily impact older women.
Umbilical hernias materialize when fatty tissue or a portion of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall close to the navel. Such hernias are frequently observed in newborns and pregnant women.
Incisional hernias, also known as ventral hernias, transpire when tissue protrudes through a scar in the abdominal area resulting from previous surgery. Unlike some hernias, incisional hernias do not resolve spontaneously and necessitate surgical intervention for correction.
An epigastric hernia materializes as a hernia type in the abdominal wall’s epigastric region, situated above the belly button and immediately beneath the sternum.
This hernia arises when the intestine pushes through the abdominal wall at the lateral side of the abdominal muscle, situated below the navel.
A diaphragmatic hernia originates from a congenital anomaly, characterized by an irregular aperture in the diaphragm.
Laparoscopic procedure : The approach to hernia repair through laparoscopy shares similarities with other laparoscopic surgeries. Utilizing a small camera and scaled-down surgical instruments, the surgeon rectifies the hernia via minor incisions in the lower abdomen. Opting for laparoscopic hernia repair reduces the likelihood of infections. Furthermore, adhering to proper post-surgery precautions is essential.
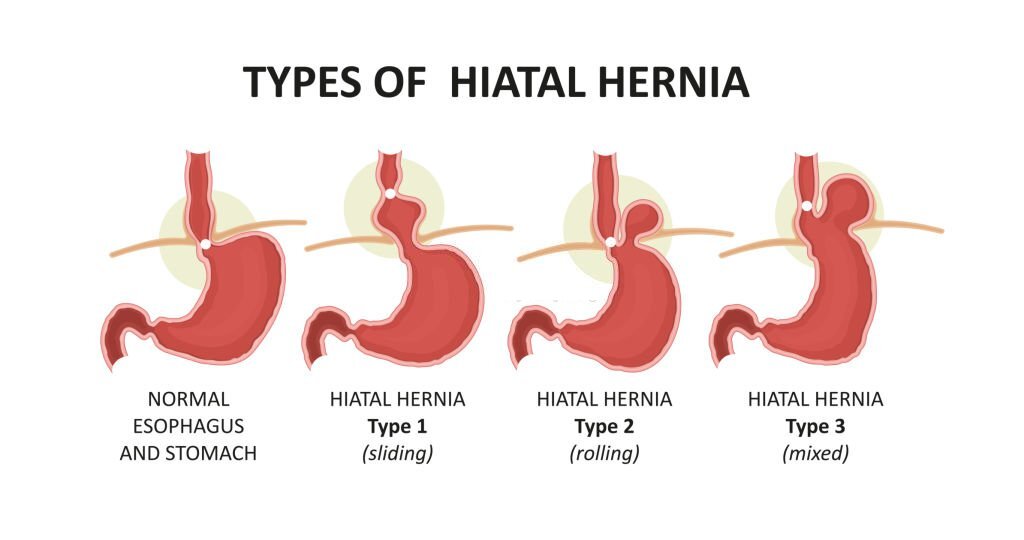
Symptoms Of Hernia
- Swelling or bulge in the groin
- Burning or aching sensation in the area of the bulge
- Pain or discomfort in the abdomen or groin, especially when bending over, coughing and playing sports, etc.
- Increase in the size of the bulge
- The feeling of weakness in the groin
Causes Of Hernia
Hernias are caused due to weakened muscles that are present since birth or associated with aging. Also, repeated strains on the abdominal and groin areas may cause a hernia.
Such strains may come by:
- Physical exercise
- Straining during bowel movements
- Pregnancy
- Chronic coughing or sneezing